Interval
Create interval plots, usually bar charts. Interval plots are good for showing how your data is trending.
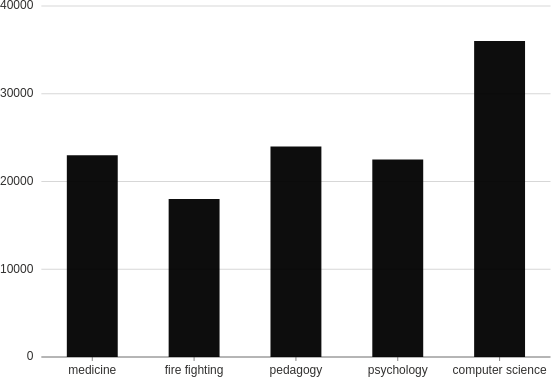
from h2o_wave import data
q.page['example'] = ui.plot_card(
box='1 1 4 5',
title='Interval',
data=data('profession salary', 5, rows=[
('medicine', 23000),
('fire fighting', 18000),
('pedagogy', 24000),
('psychology', 22500),
('computer science', 36000),
]),
plot=ui.plot([ui.mark(type='interval', x='=profession', y='=salary', y_min=0)])
)
Check the full API at ui.plot_card.
Transpose
To transpose the plot, simply switch the x and y coordinate values.
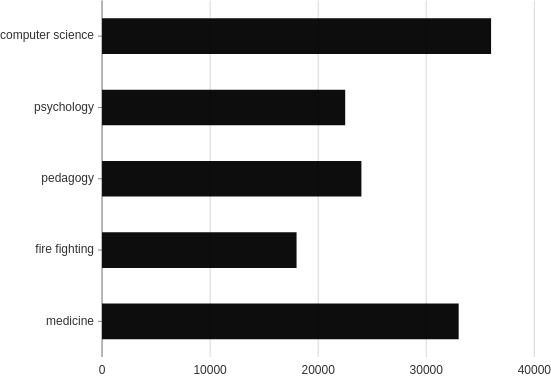
from h2o_wave import data
q.page['example'] = ui.plot_card(
box='1 1 4 5',
title='Interval transposed',
data=data('profession salary', 5, rows=[
('medicine', 33000),
('fire fighting', 18000),
('pedagogy', 24000),
('psychology', 22500),
('computer science', 36000),
]),
plot=ui.plot([ui.mark(type='interval', x='=salary', y='=profession', y_min=0)])
)
Stacked
Useful when you want to display the third dimension to your bar charts and would like to emphasize the difference in totals across columns.
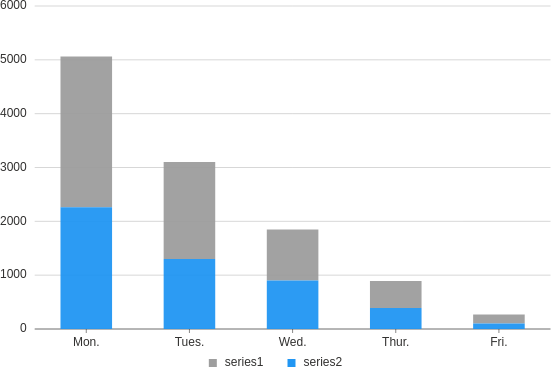
from h2o_wave import data
q.page['example'] = ui.plot_card(
box='1 1 4 5',
title='Intervals, stacked',
data=data('day type time', 10, rows=[
('Mon.','series1', 2800),
('Mon.','series2', 2260),
('Tues.','series1', 1800),
('Tues.','series2', 1300),
('Wed.','series1', 950),
('Wed.','series2', 900),
('Thur.','series1', 500),
('Thur.','series2', 390),
('Fri.','series1', 170),
('Fri.','series2', 100),
]),
plot=ui.plot([
ui.mark(type='interval', x='=day', y='=time', color='=type', stack='auto', y_min=0)
])
)
Grouped
Make a grouped column plot.
from h2o_wave import data
q.page['example'] = ui.plot_card(
box='1 1 4 5',
title='Intervals, groups',
data=data('day type time', 10, rows=[
('Mon.','series1', 2800),
('Mon.','series2', 2260),
('Tues.','series1', 1800),
('Tues.','series2', 1300),
('Wed.','series1', 950),
('Wed.','series2', 900),
('Thur.','series1', 500),
('Thur.','series2', 390),
('Fri.','series1', 170),
('Fri.','series2', 100),
]),
plot=ui.plot([ui.mark(type='interval', x='=day', y='=time', color='=type', dodge='auto', y_min=0)])
)
Stacked grouped
Make a column plot with both stacked and grouped bars.
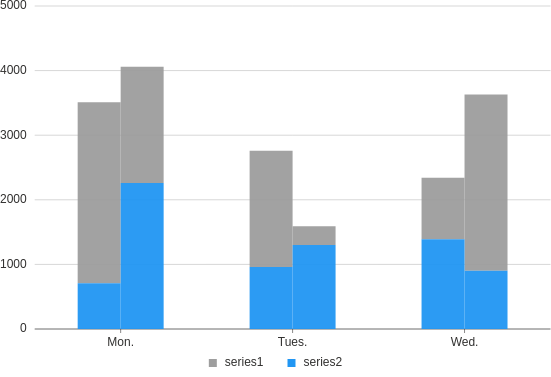
from h2o_wave import data
q.page['example'] = ui.plot_card(
box='1 1 4 5',
title='Intervals, stacked and dodged',
data=data('day type time gender', 12, rows=[
('Mon.','series1', 2800, 'male'),
('Mon.','series1', 1800, 'female'),
('Mon.','series2', 2260, 'female'),
('Mon.','series2', 710, 'male'),
('Tues.','series1', 1800, 'male'),
('Tues.','series1', 290, 'female'),
('Tues.','series2', 1300, 'female'),
('Tues.','series2', 960, 'male'),
('Wed.','series1', 950, 'male'),
('Wed.','series1', 2730, 'female'),
('Wed.','series2', 1390, 'male'),
('Wed.','series2', 900, 'female'),
]),
plot=ui.plot([
ui.mark(
type='interval',
x='=day',
y='=time',
color='=type',
stack='auto',
dodge='=gender',
y_min=0
)
])
)
Range
Make a column plot with each bar representing high/low (or start/end) values.
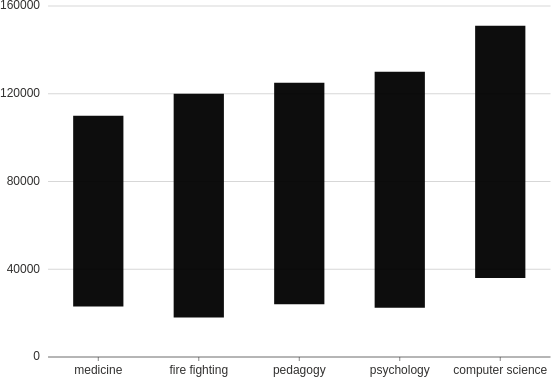
from h2o_wave import data
q.page['example'] = ui.plot_card(
box='1 1 4 5',
title='Interval, range',
data=data('profession max min', 5, rows=[
('medicine', 110000, 23000),
('fire fighting', 120000, 18000),
('pedagogy', 125000, 24000),
('psychology', 130000, 22500),
('computer science', 151000, 36000),
]),
plot=ui.plot([ui.mark(type='interval', x='=profession', y0='=min', y='=max')])
)
Gantt
Make a Gantt plot with each bar representing high/low (or start/end) values.
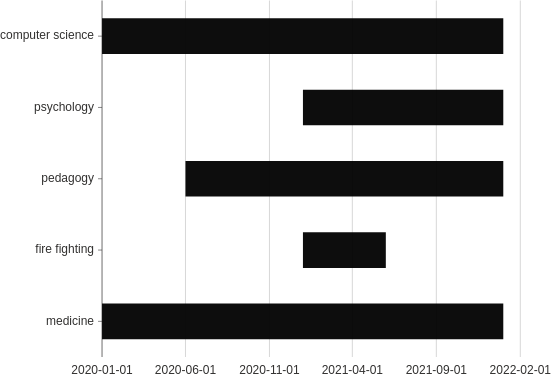
from h2o_wave import data
q.page['example'] = ui.plot_card(
box='1 1 4 5',
title='Interval, range',
data=data('profession max min', 5, rows=[
('medicine', '2022-01-01', '2020-01-01'),
('fire fighting', '2021-06-01', '2021-01-01'),
('pedagogy', '2020-06-01', '2022-01-01'),
('psychology', '2021-01-01', '2022-01-01'),
('computer science', '2020-01-01', '2022-01-01'),
]),
plot=ui.plot([ui.mark(type='interval', y='=profession', x_scale='time', x0='=min', x='=max')])
)
Polar
Make a rose plot (a bar plot in polar coordinates).
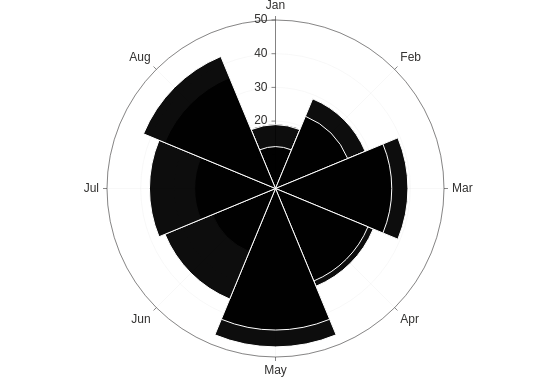
from h2o_wave import data
q.page['example'] = ui.plot_card(
box='1 1 4 5',
title='Interval, polar',
data=data('month rainfall', 16, rows=[
('Jan', 18.9),
('Feb', 28.8),
('Mar', 39.3),
('Apr', 31.4),
('May', 47),
('Jun', 20.3),
('Jul', 24),
('Aug', 35.6),
('Jan', 12.4),
('Feb', 23.2),
('Mar', 34.5),
('Apr', 29.7),
('May', 42),
('Jun', 35.5),
('Jul', 37.4),
('Aug', 42.4),
]),
plot=ui.plot([ui.mark(coord='polar', type='interval', x='=month', y='=rainfall', y_min=0, stroke_color='$card')])
)
Polar stacked
Make a stacked rose plot (a stacked bar plot in polar coordinates).
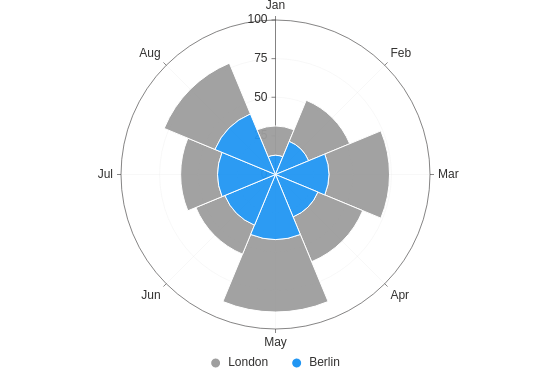
from h2o_wave import data
q.page['example'] = ui.plot_card(
box='1 1 4 5',
title='Intervals, polar, stacked',
data=data('city month rainfall', 16, rows=[
('London', 'Jan', 18.9),
('London', 'Feb', 28.8),
('London', 'Mar', 39.3),
('London', 'Apr', 31.4),
('London', 'May', 47),
('London', 'Jun', 20.3),
('London', 'Jul', 24),
('London', 'Aug', 35.6),
('Berlin', 'Jan', 12.4),
('Berlin', 'Feb', 23.2),
('Berlin', 'Mar', 34.5),
('Berlin', 'Apr', 29.7),
('Berlin', 'May', 42),
('Berlin', 'Jun', 35.5),
('Berlin', 'Jul', 37.4),
('Berlin', 'Aug', 42.4),
]),
plot=ui.plot([
ui.mark(
coord='polar',
type='interval',
x='=month',
y='=rainfall',
color='=city',
stack='auto',
y_min=0,
stroke_color='$card'
)
])
)
Theta
Make a "racetrack" plot (a bar plot in polar coordinates, transposed).
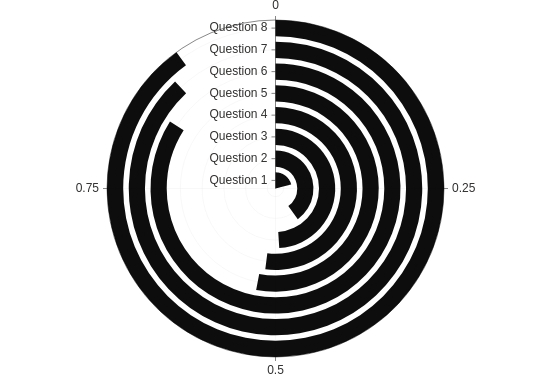
from h2o_wave import data
q.page['example'] = ui.plot_card(
box='1 1 4 5',
title='Intervals, theta',
data=data('question percent', 8, rows=[
('Question 1', 0.21),
('Question 2', 0.4),
('Question 3', 0.49),
('Question 4', 0.52),
('Question 5', 0.53),
('Question 6', 0.84),
('Question 7', 0.88),
('Question 8', 0.9),
]),
plot=ui.plot([
ui.mark(coord='theta', type='interval', x='=question', y='=percent', stack='auto', y_min=0)
])
)
Theta stacked
Make a stacked "racetrack" plot.
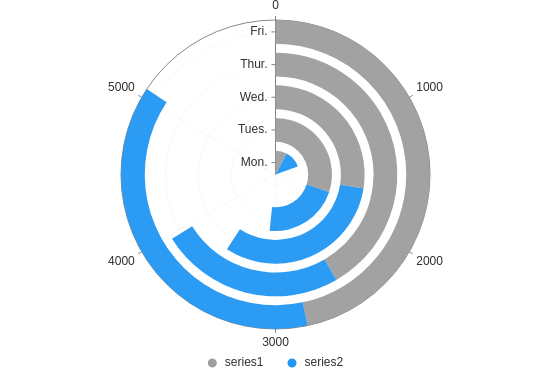
from h2o_wave import data
q.page['example'] = ui.plot_card(
box='1 1 4 5',
title='Intervals, theta, stacked',
data=data('day type time', 10, rows=[
('Mon.','series1', 470),
('Mon.','series2', 700),
('Tues.','series1', 1800),
('Tues.','series2', 1300),
('Wed.','series1', 1650),
('Wed.','series2', 1900),
('Thur.','series1', 2500),
('Thur.','series2', 1470),
('Fri.','series1', 2800),
('Fri.','series2', 2260),
]),
plot=ui.plot([
ui.mark(
coord='theta',
type='interval',
x='=day',
y='=time',
color='=type',
stack='auto',
y_min=0
)
])
)
Labels
Make a column plot with labels on each bar.
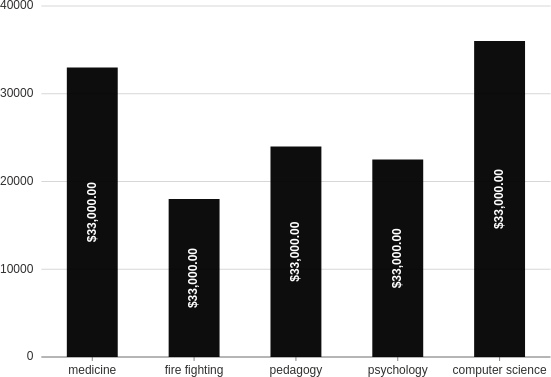
from h2o_wave import data
q.page['example'] = ui.plot_card(
box='1 1 4 5',
title='Label Customization',
data=data('profession salary', 5, rows=[
('medicine', 33000),
('fire fighting', 18000),
('pedagogy', 24000),
('psychology', 22500),
('computer science', 36000),
]),
plot=ui.plot([
ui.mark(
type='interval',
x='=profession',
y='=salary', y_min=0,
label='=${{intl salary minimum_fraction_digits=2 maximum_fraction_digits=2}}',
label_offset=0, label_position='middle', label_rotation='-90', label_fill_color='#fff',
label_font_weight='bold'
)
])
)
Helix
Make a bar plot in helical coordinates.
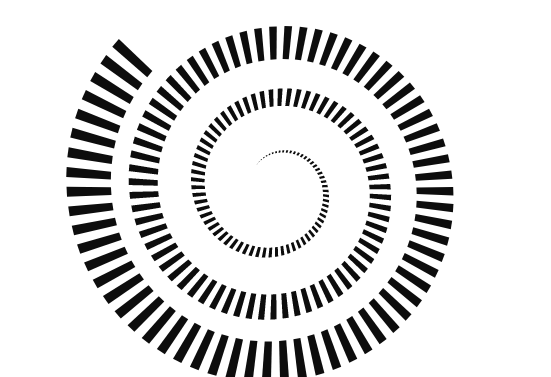
from h2o_wave import data
q.page['example'] = ui.plot_card(
box='1 1 4 5',
title='Interval, helix',
data=data('product price', 200, rows=[ (f'P{i}', i) for i in range(200)]),
plot=ui.plot([ui.mark(coord='helix', type='interval', x='=product', y='=price', y_min=0)])
)
Histogram
Best used for numerical data when the shape of the distribution is needed.
from h2o_wave import data
q.page['example'] = ui.plot_card(
box='1 1 4 5',
title='Interval, range',
data=data('price low high', 8, rows=[
(4, 50, 100),
(6, 100, 150),
(8, 150, 200),
(16, 350, 400),
(18, 400, 450),
(10, 200, 250),
(12, 250, 300),
(14, 300, 350),
]),
plot=ui.plot([ui.mark(type='interval', y='=price', x1='=low', x2='=high', y_min=0)])
)